|
|
PKI
pages
Today's
IT's key problem became the data security and authentication
The computer networks growth (internet), the creation of the eBussines
and money transactions needs a securized data environment which
is easy to use and is based on laws. The easy use part was provided
by the technological growth legacy part was provided by the international
laws which made possible the electronical signatures appearance.
The European Union's Committee 93/1999 Directive defines on European
level the requests for digital handling of the documents. The EU
takes care of the harmonization of the standards (ETSI, CEN ISSS,
EESSI, IST).
The
PKI system, as it names shows too (Public Key Infrastructure), offers
an application environment which enables a two key authentication
and data securing procedures for computers.
The
advantages of using the PKI systems comes from the legacy, it enables
the authentication of official documents like bank wires, orders,
bills etc. By using the PKI systems and the smart cards the IT environment,
data transfers could be secured without reducing their maneuverability
and simplity. In many cases this simplity reduces the secure applications
when in a place of many system's passwords and users we can use
a simply smartcard. This means a significant reduce of the costs
if in a place of many systems we need to maintain only the PKI based
smartcard. By reducing the administration we increase the security.
The
encrypt and authenticate the electronic data works on a unified
theory, which is called PKI system. In the system the users has
two keys, a private key which is known and owned (ex. on smartcard)
only by the user and a public key which could be reached by anybody
and it is saved into a well accessed place (ex. meta directory).
With the combination of these keys you can create a digital signature
and encrypt critical data, so the receiver will need only the sender's
public key to decrypt the data. The private key is always stored
in secret, in this way the transaction will remain safe. The private
and public keys must be certified. This is made by a Certification
Authority as a third person- who authenticates, signs and supplies
a certification to the keys.
General context, functionality
The
general context of the PKI system is presented in the following
picture:
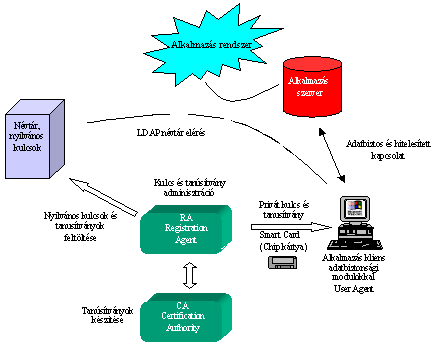 PKI
PKI based systems PKI
PKI based systems
The creation of private
and public keys could be done in many places.
The creator could be CA, RA or the keys could be generated on smart cards,
which advantage stands in the fact that the private key will never
leave the smartcard. The public keys are stored in meta directories,
the private keys are on smart cards or other mobile media. The administration
by users of the key pairs can be made by RA, which ensures the massive
sending of the keys into meta directories. The CA prepares the certifications,
it certifies as a third person the private keys of the users. The
certification requests are sent by the RA to CA, the CA sends the
certification for keys back to the RA, the certifications will be
added to the private and public keys.
On the clients application side security modules
makes the achieving, pairing of the keys and the encryption of
the data. Near the utility functions appears the possibility to sign
and encrypt documents. When the application clients uses the public
keys, reaches the meta directories via the LDAP protocols.
In the meta directory are saved the public keys
of all users who has taken a part in the authentication.
At the authentication process the application client
reads the private key from a smartcard, reaches the meta directory
over the LDAP protocol for the public key and with this key creates
the digital-signature. With the combination of the keys the data
could be encrypted.
On the receiver's part the application client or
server by a combination of it's private and public keys and the
sender's public key reaches the encrypted data and verifies the
authenticity of the sender. The application could be any kind, the
encrypted data handling is only between the application users. At
the WEB based applications the authentication and encryption procedures
are similar, the differences are in the data security and authentication
modules which are representative for the on-line technology.
Key creation
A
basic security problem is the key creation place, which is on all
PKI elements. The progress of the PKI systems allows many PKI elements.
Generally there are two possibilities to create key pairs (centralized
and decentralized), and both has it`s advantage and disadvantage
from the view of the CA and the user.
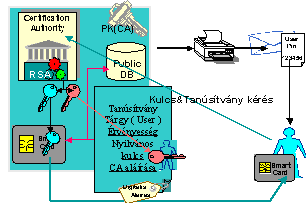
Centralized key-pair creation
If the keys are created
at CA we call the creation centralized, if the creation is on the
user's side or RA it calls decentralized or local key-pair creation.
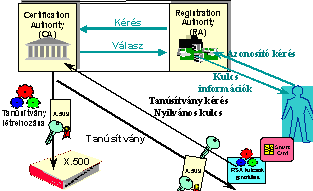
Local
key-pair creation
The
most secure way to create key-pairs is to save the key pairs on
a smartcard which are able to generate the keys too. This method
is called on-board key generation. The security of the method come
from the fact that the private key will never leave the card. The
public key will reach in the same way to the CA. For it's security
issues it will be the future choice to create key-pairs.
The
presentation of the PKI system's elements
As
we mentioned in the introduction the PKI offers a secure and law
supported environment which enables two key using third person security
and authentication applications. PKI elements are important application
integration elements. To introduce this technology to an organization
is effects of the current and future electronic document managing
applications. The independent part of the CA, RA and user modules
(clients) will be showed below, these elements in practice could
be integrated deeply in the application and to change it's functions.
We
consider meta directories as PKI elements too, but they aren't a
part of this technology. The meta directory technology is an independent
technology and it reaches an important implementation role nowadays.
They are a current implementation environment of the PKI systems,
so this is why we will present this technology near the PKI elements.
CA
The evolution of the PKI systems stands in the
differences of the CA and RA functions. In the first generation
PKI systems there was no RA unit-, registration was took by the
CA. In the next generations (second, third, forth) the RA takes
more and more administrative functions and takes the policy management
too. The separation of the CA and RA functions stands on the system's
generation, so this forth generation separation isn't true for all
producers.
The
most important functions of CA
:
•
RSA
key pair generation
•
CA
signed X.509 certificates
•
public key binding to persons
• Certificate
Revocation List creation
•
database
and meta directory handling
•
master
key usage
CRL
(Certificate Revocation List): the list of the revoked certifications.
The revocation generally comes from the RA, after it the certification
will be unusable. The revocation reasons could be: the owner lost
the smartcard, the requested service was stopped or the CA key was
compromised. The most important problem of the policy is the frequently
update and release of the CRL. Necessary to regulate the maximum
validity period of CRL and certification expiry date, and to release
frequently the CRL in a public, easy to access place. The release
of CRL is generally in X.500 directories, which can be reached periodically
by the applications.
RA
In
the forth generation of PKI the RA became the administrative and
effective center. Generally the CA appears as a service.
The
most important functions of RA:
•
user
identifier generation
•
user
key request from CA
•
user
key reception from CA
•
user
key storing in file
•
user
key storing in a smartcard
•
certification
revocation request from CA
•
user
management policy
•
user
key renewal
•
key restoring
•
user
deletion
•
logging
•
user key storing (on smart cards or PKCS#12 key files)
•
smartcard
release, management
•
policy
file exports
•
user
certification request
•
request
revocation
•
mass
key maintaining (batch)
The
creation of policy management is very important for the PKI system's
management, because it is about key management and coordination
of system element functional rights. The maintaining of the policy
management is at the RA which ensures the related communication
with the other elements of the system.
User
Agent ( PKI client)
The
User Agent is an application
which runs on the end-user side and enables the users key, smartcard
authentication based operations. These operations could be done
only by user and are described by the RA. The client functions depends
on the PKI generation too. In newer versions the clients has more
functions which are described by the policy management.
Typical
function of the User Agent:
•
digital
signature creation
•
encryption,
decryption
•
authentication
•
certificate
request
•
key
renewal request
•
key
revocation request
•
local
RSA key pair generation, smartcard allocation
The
data security modules can be connected to other applications, you
can read more about this in the PKI enabled application chapter,
the integration of the client become so deeply so the handling of
the client will be only from these application.
PKI
enabled systems
What
does PKI enabled means? Functionally it means the usage of two keys
encryption based coding and authentication applications in different
data security and authorizing situations. In practice this means
that you can enter with only one smartcard to many applications
and you can digitally sign or encrypt in many ways. The PKI authentication
and data security applications could be integrated in other data
security environments. This chapter try to present the essence of
the PKI enabling applications.
The digital signature and encryption
for mail, MS-Office, Notes documents
The
generally used electronic document handling environment implemented
PKI clients and card handling modules with enables the simple generation
of the digital signature and it`s use. The command of the modules
could be done from additional buttons or dialogue panels.
Application
implementable PKI modules (toolkits)
In
every application where the partners want to change electronical
data should use digital signature. This kind of application could
be different, but to be implement PKI functionality, the PKI modules
are added like PKI toolkit or plugins into the system. In this case
the PKI modules are completely commanded by a certain application
and the PKI service will be available only from the application's
interface.
Computer start
and application login authentication and data encryption
Certified
login authentication enabling into computers and certain applications.
The smart cad based login represents a high level security at the
critical application maintenance or administration. There is a
possibility to access many different security level applications
by a simple smartcard, which reduces the administration time of
many passwords and accessing levels. The PKI technology ensures
the local data local encryption (ex. hard disk).
Local area
networks security
PKI
technology can be applied to allow access to the local network resources
to encrypt running data. To reach several of file groups (file server)
applications (application server) at the local server side could
be implemented by authentication (ex. Network password, resource
access password). All of these operations became much more reliable
and secure together with PKI smartcard technology. This technology
can ensure the security of the server environments where a simple
password based software applications are not enough. The smartcard
which used for a local machine access is could be used for network
access too, which can reduce the password administration efforts.
Authentication
and security over VPN networks
The
VPN are created when the network was created on public network (like
internet) and the virtual network needs to be closed. The VPN uses
additional security operations for the virtual network data and
access protection, which could be done by using PKI technology.
WEB authentication
In practice it
means smartcard enabled WEB access. In this case the PKI modules
are implemented into the browser compatible WEB applications.
Single-Sign On
The
digital signature authenticates the user in any case, so the user
can access all the authentication needed systems with this unique
operation.
It means that by using the same smartcard the user can access computers,
networks, buy from WEB, use the companies VPN network from home,
to encrypt the notebooks data or enter into the company at the card
authentication door etc. The essential is that the user can access
electronic services by using a simple digital signature.
|
|
|




